Car audio systems are among the most frequently used entertainment features in a vehicle and play a central role in the smart cockpit experience. They not only provide enjoyable listening during travel but also represent a rapidly evolving technology that continuously enhances the overall driving experience.
Understanding Sound
The sounds our ears perceive originate from object vibrations, transmitted through a medium, and finally processed by our auditory nervous system into recognizable sound. Sound has three fundamental characteristics:
-
Pitch: Determined by frequency; higher frequency means higher pitch.
-
Loudness: Related to amplitude and distance; greater amplitude or closer proximity means louder sound.
-
Timbre: Determined by the sound source's characteristics, helping us distinguish between different instruments or voices.
The human ear typically perceives frequencies from 20Hz to 20kHz. Taking a human voice as an example, the 100–300Hz range affects fullness, 1k–5kHz enhances vocal clarity, and frequencies above 7kHz add brightness.
Components of a Car Audio System
A complete car audio system includes speakers, an amplifier, system design, algorithms, and tuning.
1. Car Speakers
Speakers are the key components that convert electrical signals into sound. Because high and low-frequency sounds have different reproduction requirements, cars typically use a multi-speaker setup with dedicated speakers for specific ranges:
-
Tweeters (2048–20kHz): Enhance detail and clarity.
-
Mid-range Speakers (256–2048Hz): Reproduce most vocals and recognizable sounds.
-
Woofers (60–256Hz): Add rhythm and mask road noise.
-
Subwoofers (16–60Hz): Create a powerful, deep bass impact.
Speakers also come in coaxial (full-range) and component (separate tweeter and mid-woofer) types, with the latter often offering superior sound quality.
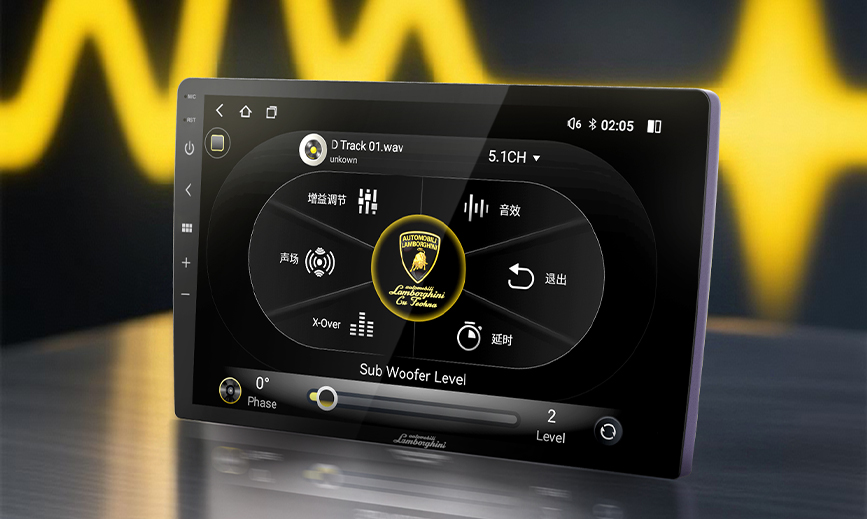
2. Car Amplifier
The amplifier acts as the "brain" of the audio system. It amplifies the audio signal, improves sound quality, and powers the speakers. Compared to built-in head unit amplifiers, external amplifiers deliver more power and often feature a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) for advanced functions like noise cancellation and sound field optimization.
3. Audio System Design
System design focuses on speaker placement and channel configuration, aiming to provide an immersive listening experience for all passengers. Common channel types include:
-
Stereo (4–7 speakers)
-
Surround Sound (8–15 speakers)
-
Immersive Audio like Dolby Atmos (16+ speakers), which uses overhead and subwoofer speakers to create a three-dimensional soundstage.
4. Audio Algorithms & Tuning
The complex interior cabin space can cause phase and time alignment issues, affecting sound quality. Audio algorithms use digital tuning to compensate for these problems, optimizing frequency response and sound imaging so all passengers experience balanced, realistic sound.
Professional tuning by audio engineers, using both instrument measurements and subjective listening tests, fine-tunes the system to ensure the sound is both accurate and emotionally engaging.
By effectively combining hardware design with software calibration, modern car audio systems can deliver a music experience rivaling live performances, making them an essential part of today's intelligent vehicles.